
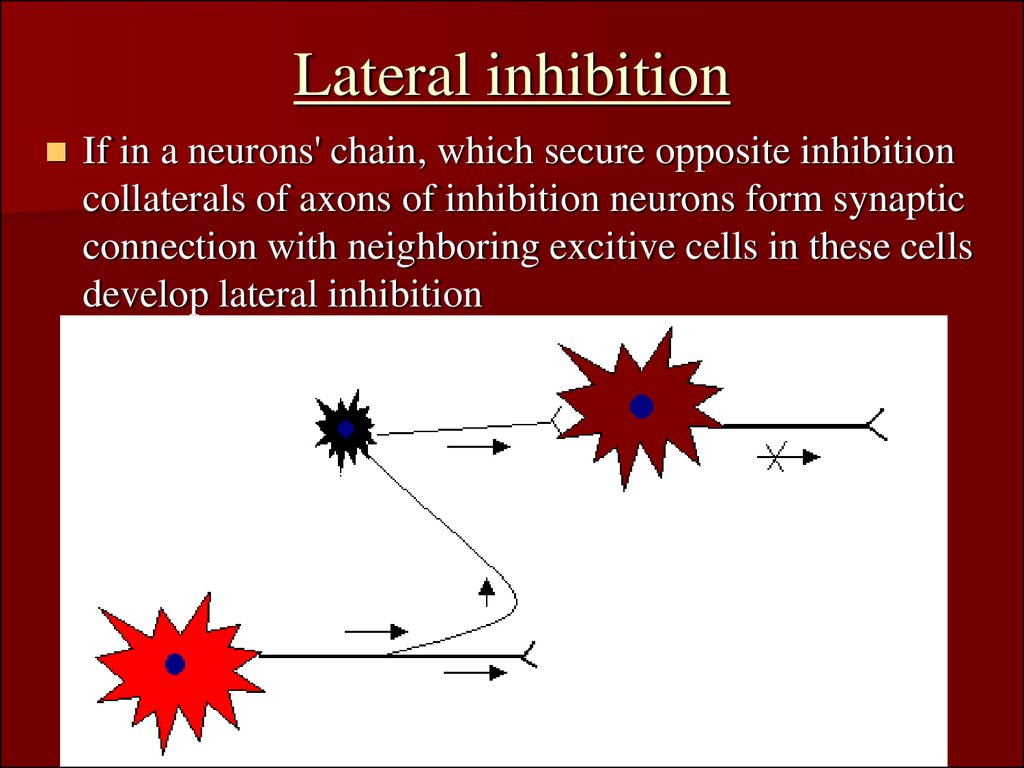
As a result, the action potential signal "jumps" along the axon membrane from node to node rather than spreading smoothly along the membrane, as they do in axons that do not have a myelin sheath. In myelinated neurons, ion flows occur only at the nodes of Ranvier. During the refractory period, another action potential cannot be generated The nerve goes through a brief refractory period before racing resting potential. \)shows the change in potential of the axon membrane during an action potential. Glial cells also remove any debris by phagocytosis. Instead they maintain homeostasis, form myelin, and provide support and protection for neurons. Biology Anatomy Nervous System Which of the following are the parts of neurons A) brain, spinal cord, and vertebral column B) dendrite, axon, and cell body C) sensory and motor D) cortex, medulla and sheath E) sympathetic and parasympathetic 2 A dendrite conducts nerve impulses the cell body.
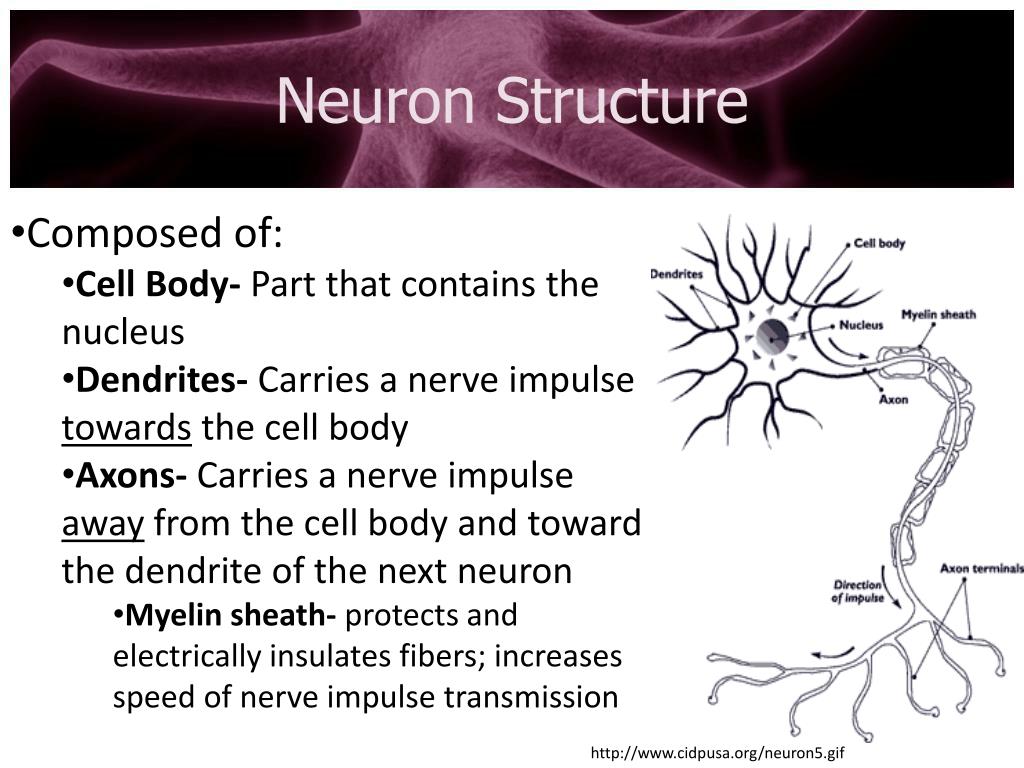
The part of the neuron that conducts nerve impulses toward the cell body is the. Neurons: Structure and Types Synaptic Transmission of Nerve. The side branch of an axon is referred to as the. Glial cells do not transmit nerve impulses. Axons Ganglia Dendrites None of the above Dendrites are branched projections of the cell body. Myelin sheath is produced by glial cells. This results in loss of strength and co-ordination in the limbs. This causes damage to motor neurons which means that muscles no longer receive signals from the brain or spinal cord. When a nerve impulse or action potential reaches the axon terminal, synaptic transmission occurs via an electrical or chemical synapse. The axon is the long threadlike portion of the neuron which conducts the. It continues from birth to adolescence.Ĭertain diseases, such as multiple sclerosis and poliomyelitis, cause the myelin sheath to be destroyed. Nerve impulse conduction refers to the propagation of nerve impulse that occurs due to a change in membrane potential beyond the cell membrane. From the cell body, the electrical impulse is transmitted to the axon. Myelination is the process of myelin developing around the axon fibres.

The junction across which a nerve impulse passes from an axon terminal to a neuron, muscle cell, or gland cell. the appendage of the neuron that transmits impulses away from the cell body. A rock or mineral bearing such a mark or marks. The fatty sheath increases the speed of the nerve impulses along the neuron. a junction between two nerve cells, consisting of a minute gap across which impulses pass by diffusion of a neurotransmitter. The axon is insulated by a fatty ( myelin ) sheath. The axons of peripheral neurons that travel a common route are bundled together to form nerves. In cytology terms the difference between dendron and dendrite is that dendron is a slender projection of a nerve cell which conducts nerve impulses from a synapse to the body of the cell a dendrite while dendrite is slender cell process emanating from the cell bodies of dendritic cells and follicular dendritic cells of the immune system. dendrites - branched nerve fibres which receive nerve impulses and pass them towards a cell body. The cell bodies of other PNS neurons, such as the sensory neurons that provide information about touch, position, pain, and temperature, are located outside of the CNS, where they are found in clusters known as ganglia.

An impulse is an electrical signal that travels along a neuron.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
